
Hyperinflation In Economics Assignment Point Hyperinflation describes rapid and out of control price increases in an economy that result in extreme inflation. learn the causes and how it can impact consumers. What is hyperinflation? in economics, hyperinflation is used to describe situations where the prices of all goods and services rise uncontrollably over a defined time period. in other words, hyperinflation is extremely rapid inflation. generally, inflation is termed hyperinflation when the rate of inflation grows at more than 50% a month.
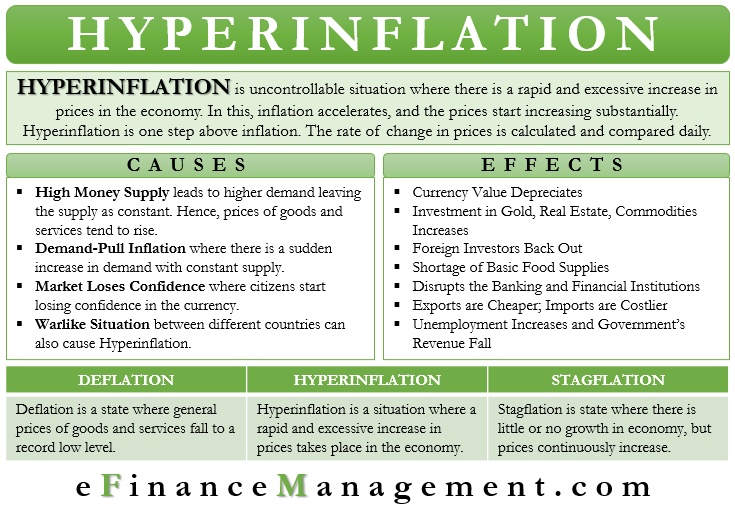
Hyperinflation Meaning Causes Effects Examples Conclusion Efm In economics, hyperinflation is a very high and typically accelerating inflation. it quickly erodes the real value of the local currency, as the prices of all goods increase. this causes people to minimize their holdings in that currency as they usually switch to more stable foreign currencies. [1]. In a nutshell, it is incredibly rapid inflation. if you were living in a country gripped by hyperinflation, you’d know about it. it refers to a situation where the prices of goods and services rise uncontrollably over a defined period of time. in general, the term is used when the rate of inflation increases at more than 50% a month. When prices soar over 50% in one month, the economy is experiencing hyperinflation. hyperinflation can be caused by a government that prints more money than its nation’s gdp can support. hyperinflation tends to occur during a period of economic turmoil or depression. demand pull inflation can also cause hyperinflation. Hyperinflation is an extreme and rapid increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. it is characterized by extremely high and accelerating inflation rates, typically exceeding 50% per month.

Hyperinflation Question Armstrong Economics When prices soar over 50% in one month, the economy is experiencing hyperinflation. hyperinflation can be caused by a government that prints more money than its nation’s gdp can support. hyperinflation tends to occur during a period of economic turmoil or depression. demand pull inflation can also cause hyperinflation. Hyperinflation is an extreme and rapid increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. it is characterized by extremely high and accelerating inflation rates, typically exceeding 50% per month. Hyperinflation is a cataclysmic economic phenomenon characterized by an extreme and rapid rise in prices, causing a loss of purchasing power in a currency. excessive money supply, loss of confidence in the currency, government deficit spending, and political instability are the primary causes of hyperinflation. Hyperinflation reduces an economy’s efficiency by driving people away from monetary transactions and toward barter. in a normal economy, using money in exchange is highly efficient. during hyperinflations people prefer to be paid in commodities in order to avoid the inflation tax. Hyperinflation is a monetary condition when a country experiences an exceptionally high rate of inflation as measured by a consumer price index or other similar. Hyperinflation vs. high inflation vs. normal inflation. hyperinflation is an extreme form of inflation characterized by price increases exceeding 50% per month. for instance, something that costs $10 in january could cost $25 by march and $115 by july—just six months later. for comparison:.

Hyperinflation Economics Stock Photography Cartoondealer 232998344 Hyperinflation is a cataclysmic economic phenomenon characterized by an extreme and rapid rise in prices, causing a loss of purchasing power in a currency. excessive money supply, loss of confidence in the currency, government deficit spending, and political instability are the primary causes of hyperinflation. Hyperinflation reduces an economy’s efficiency by driving people away from monetary transactions and toward barter. in a normal economy, using money in exchange is highly efficient. during hyperinflations people prefer to be paid in commodities in order to avoid the inflation tax. Hyperinflation is a monetary condition when a country experiences an exceptionally high rate of inflation as measured by a consumer price index or other similar. Hyperinflation vs. high inflation vs. normal inflation. hyperinflation is an extreme form of inflation characterized by price increases exceeding 50% per month. for instance, something that costs $10 in january could cost $25 by march and $115 by july—just six months later. for comparison:.
